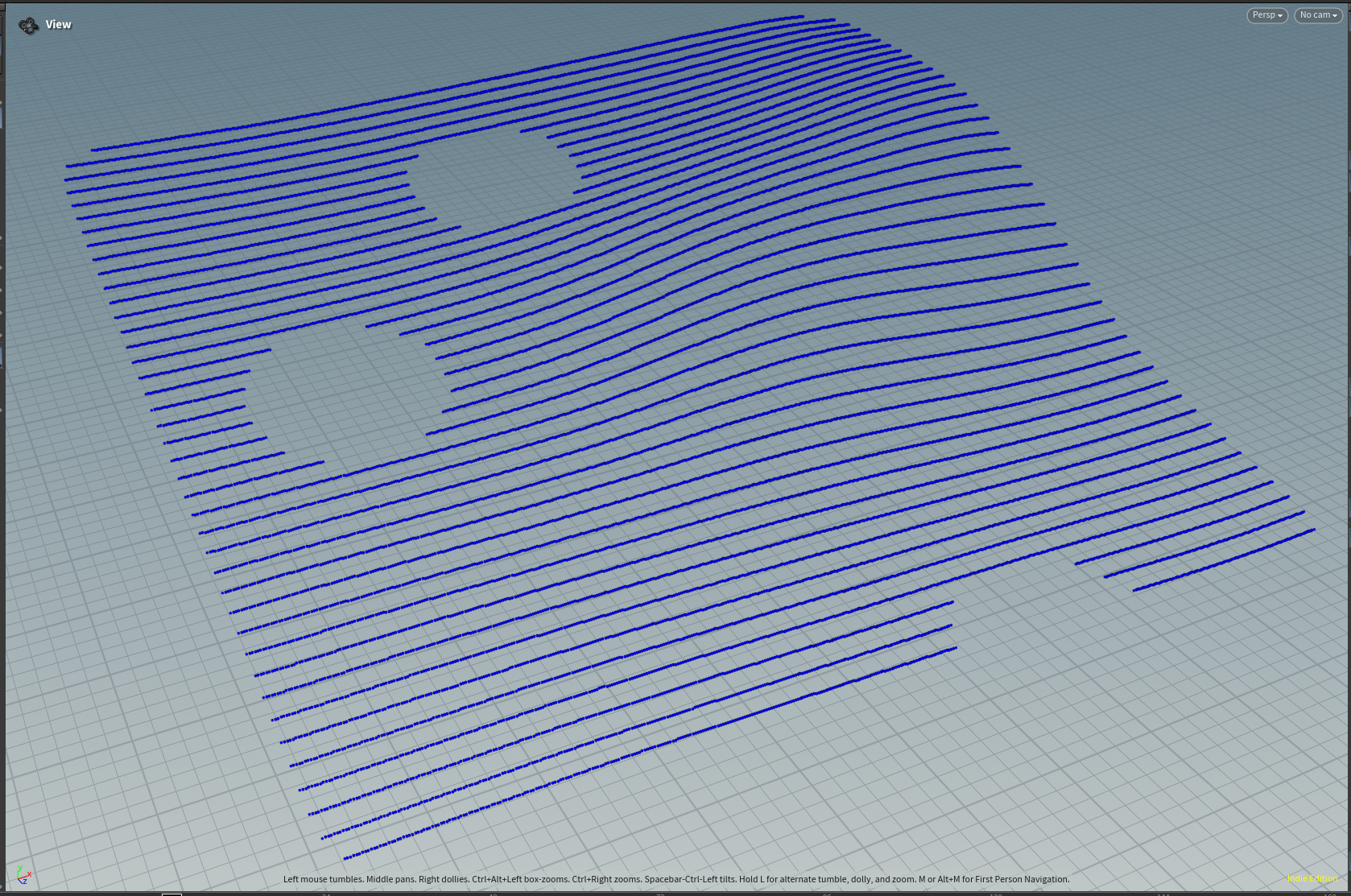
Custom Houdini Node: Delete Outliers
A while back I ran into a situation where I wanted to delete all prims with an abnormal length.
Now a simple way to do this would be to just pick some arbitrary bounding length and then delete everything outside of the bounds; however, I wanted to see if I could come up with a slightly more robust solution, that will not break if the scale of the data you are working with changes. I ended up implementing a new custom node, delete outliers, that can remove either points or prims based on the value of a particular attribute.
The node itself is fairly simple, just a wrapper around detail wrangle node with some special controls:
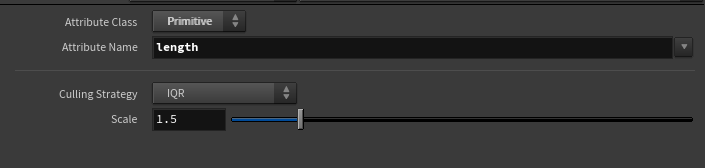
I implemented two different methods of computing outliers: IQR and Standard Deviation. I’m not a statistician and generally have a loose grasp on how these methods work, but the general explanation on the difference between these two is that IQR works better for skewed data and Standard Deviation works better for normally distributed data. You can read more about these methods here.
Here’s the VEX code:
function float[] compute_quantiles(float data[])
{
float result[];
float sorted_data[] = sort(data);
int ld = len(data);
int n = 4;
int m = ld + 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int j = i * m / n;
if (j < 1)
{
j = 1;
}
else if (j > ld-1)
{
j = ld-1;
}
int delta = i*m - j*n;
float interpolated = (sorted_data[j-1] * (n - delta) + sorted_data[j] * delta) / (float)n;
append(result, interpolated);
}
return result;
}
int attribute_class = chi("../attribute_class");
string attribute_name = chs("../attribute_name");
int outlier_method = chi("../outlier_method");
int count = 0;
float vals[] = array(); // assume floats for now.
if (attribute_class == 0) // point
{
count = npoints(0);
resize(vals, count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < count; idx++)
{
vals[idx] = point(0, attribute_name, idx);
}
}
else if (attribute_class == 1) // prim
{
count = nprimitives(0);
resize(vals, count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < count; idx++)
{
vals[idx] = prim(0, attribute_name, idx);
}
}
float lower_bound = 0.0;
float upper_bound = 0.0;
if (len(vals) >= 2)
{
if (outlier_method == 0) // IQR (performs better for skewed data)
{
float quantiles[] = compute_quantiles(vals);
if (len(quantiles) == 3)
{
float q1 = quantiles[0];
float q3 = quantiles[2];
float iqr = q3 - q1;
// if iqr is super tiny, give it a bit more wiggle room
iqr = max(iqr, 0.001);
float scale = ch("../iqr_scale");
lower_bound = q1 - (scale * iqr);
upper_bound = q3 + (scale * iqr);
@lb = lower_bound;
@ub = upper_bound;
}
}
else if (outlier_method == 1) // std deviation (performs better for normally distributed data)
{
float mean = avg(vals);
float sum_squared_distance = 0.0;
int num_samples = len(vals);
for (int idx = 0; idx < num_samples; idx++)
{
float distance = vals[idx] - mean;
sum_squared_distance += (distance * distance);
}
float standard_dev = sqrt(sum_squared_distance / num_samples);
int z_score = chi("../deviations");
lower_bound = mean - (z_score * standard_dev);
upper_bound = mean + (z_score * standard_dev);
}
}
if (!(lower_bound == upper_bound && upper_bound == 0))
{
for (int idx = 0; idx < len(vals); idx++)
{
float current_val = vals[idx];
if (current_val >= lower_bound && current_val <= upper_bound)
{
continue;
}
if (attribute_class == 0) // point
{
// should be safe to remove in place since the
// attribute wrangle is treated as an atomic operation.
removepoint(0, idx);
}
else if (attribute_class == 1) // prim
{
// should be safe to remove in place since the
// attribute wrangle is treated as an atomic operation.
removeprim(0, idx, 1);
}
}
}
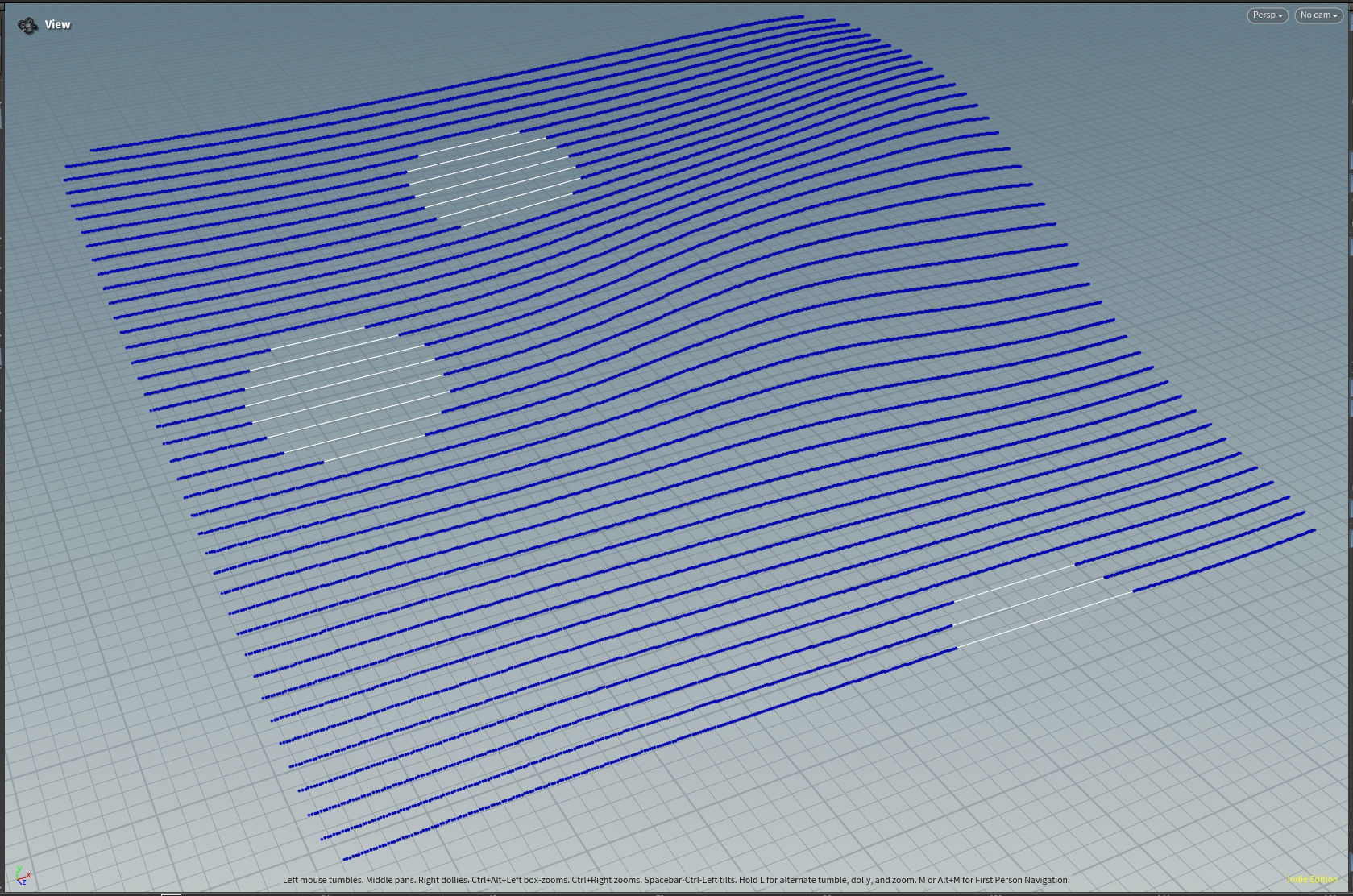
And the final result: